Thermal Engines and Machines
The area of knowledge "Thermal Engines and Machines" focuses on the study, design, analysis, and optimization of machines and engines that convert thermal energy into mechanical work, as well as machines that produce cooling/heating through refrigeration systems/heat pumps. This includes a wide range of devices such as internal combustion engines, gas turbines, rocket engines, and heating and cooling systems. The main topics of study can be grouped into:
Technical Thermodynamics
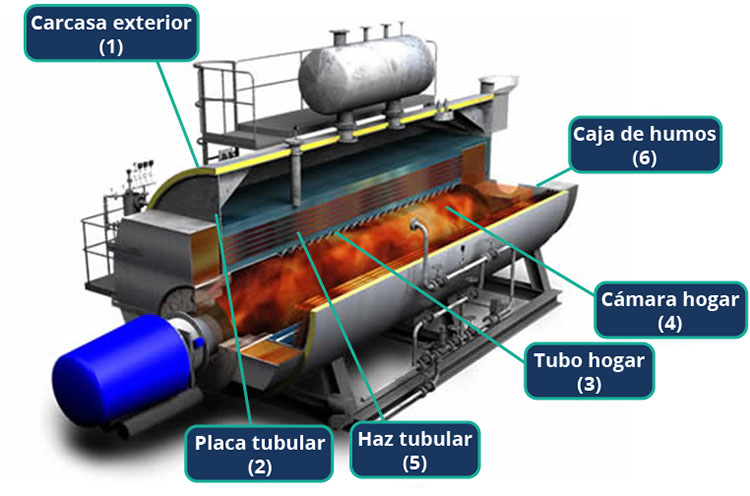
The principles of thermodynamics applied to energy conversion systems are studied. This includes thermodynamic cycles (such as the Carnot cycle, Otto cycle, Diesel cycle, Rankine cycle, Brayton cycle, Refrigeration cycles, etc.), properties of substances, exergy analysis, power generation systems, refrigeration and heat pump systems, reactive mixtures and psychrometry, reactive mixtures and combustion, as well as chemical and phase equilibriums. Technical thermodynamics also covers thermal systems such as boilers, furnaces, dryers, etc. This area primarily includes the subject Thermal Engineering.
Heat and Mass Transfer
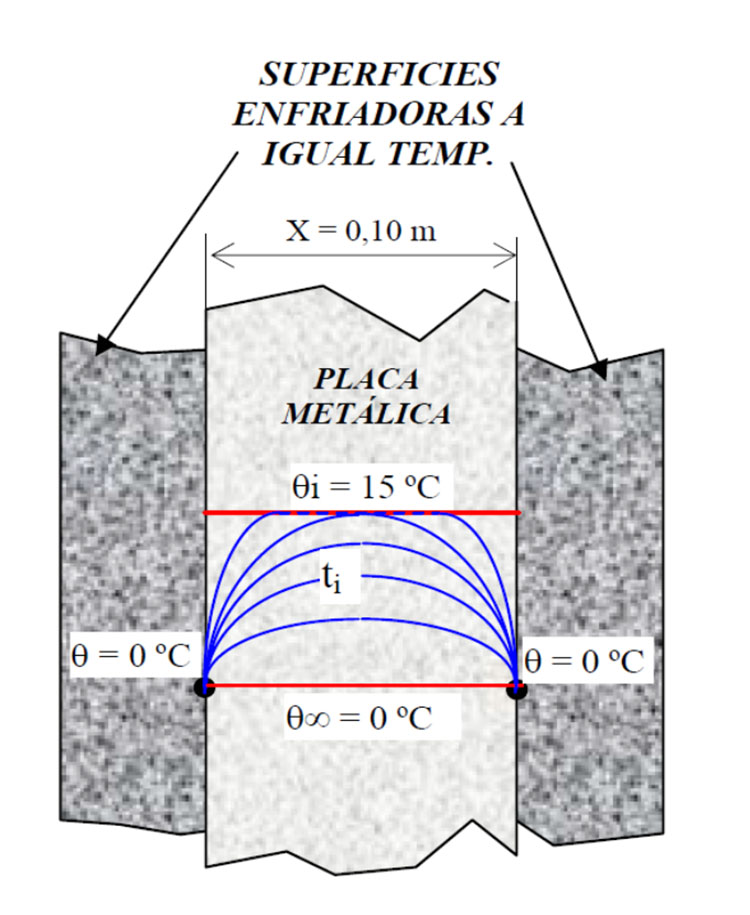
The three forms of heat transfer—conduction, convection, and radiation—are studied, along with mass transfer by diffusion. The most used correlations for solving practical heat and mass transfer problems in engineering are developed, including solutions using numerical methods (see Figure 2).
Internal Combustion Engines
The operation of gasoline and diesel engines is analyzed, including the dynamics of combustion processes, pollutant emissions, and methods for improving efficiency and reducing pollution. The analysis also includes the replacement of these fuels with less polluting alternatives.
Turbomachinery
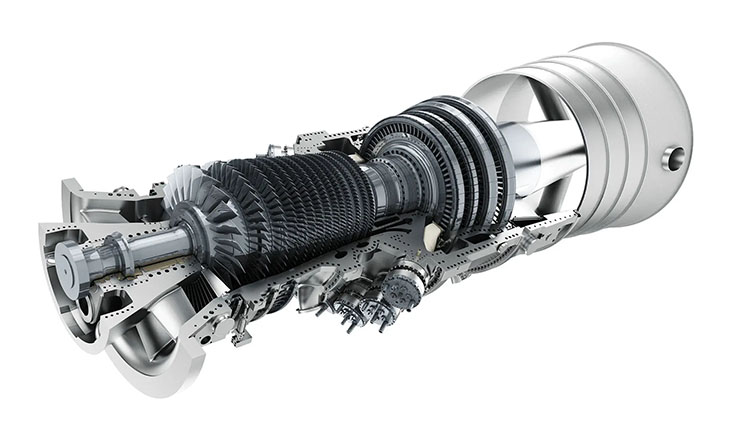
Gas turbines, steam turbines, and compressors are studied, with an emphasis on their design, operation, and applications in various industries such as mechanical/electrical power generation and aircraft propulsion.
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning
The principles of refrigeration and air conditioning are addressed, including refrigeration cycle systems, heat pumps, and advanced refrigeration technologies.
Thermal Power Plants and Cogeneration
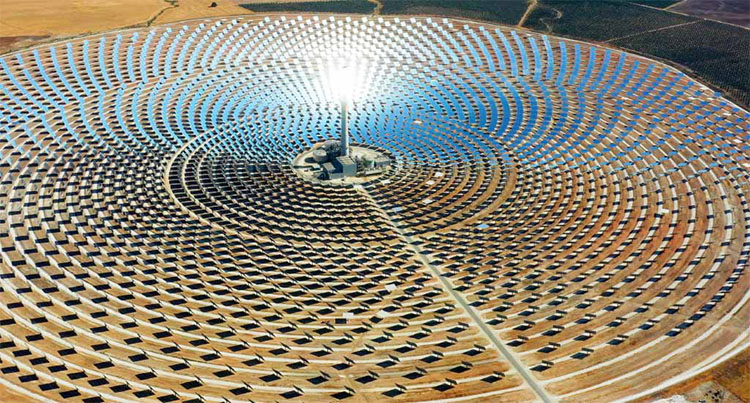

The main types of plants used for electricity generation from different heat sources are discussed, including combined cycle plants, nuclear power plants, fossil fuel plants with Rankine cycle, solar thermal plants, biomass plants, etc. In this field, cogeneration plants are also notable, which can simultaneously produce heat and electricity, and trigeneration plants, which can produce heat, cooling, and electricity.
Renewable Energy and Sustainability
The applications of thermal machines and engines in renewable energy systems, such as solar thermal energy and geothermal energy, are explored, as well as techniques to increase sustainability and energy efficiency.
The field faces challenges related to energy efficiency, reducing pollutant emissions, and integrating renewable energy technologies. Recent advancements include the development of more efficient engines, the use of advanced materials to withstand high temperatures, and the implementation of smart control systems to optimize the performance of industrial processes and thermal machines.
In summary, the area of "Thermal Engines and Machines" is vital for multiple industrial sectors and plays a key role in the transition towards more efficient and sustainable energy systems.
